Submersible pumps are engineered to operate fully submerged in liquid, making them one of the most efficient and reliable solutions for fluid handling across industrial, agricultural, municipal, and environmental applications. Their advanced design allows consistent performance under high pressure, harsh conditions, and continuous-duty cycles, positioning submersible pumps as a critical component in modern water and wastewater management systems.
Design and Engineering of Submersible Pumps: Materials, Technology, and Applications
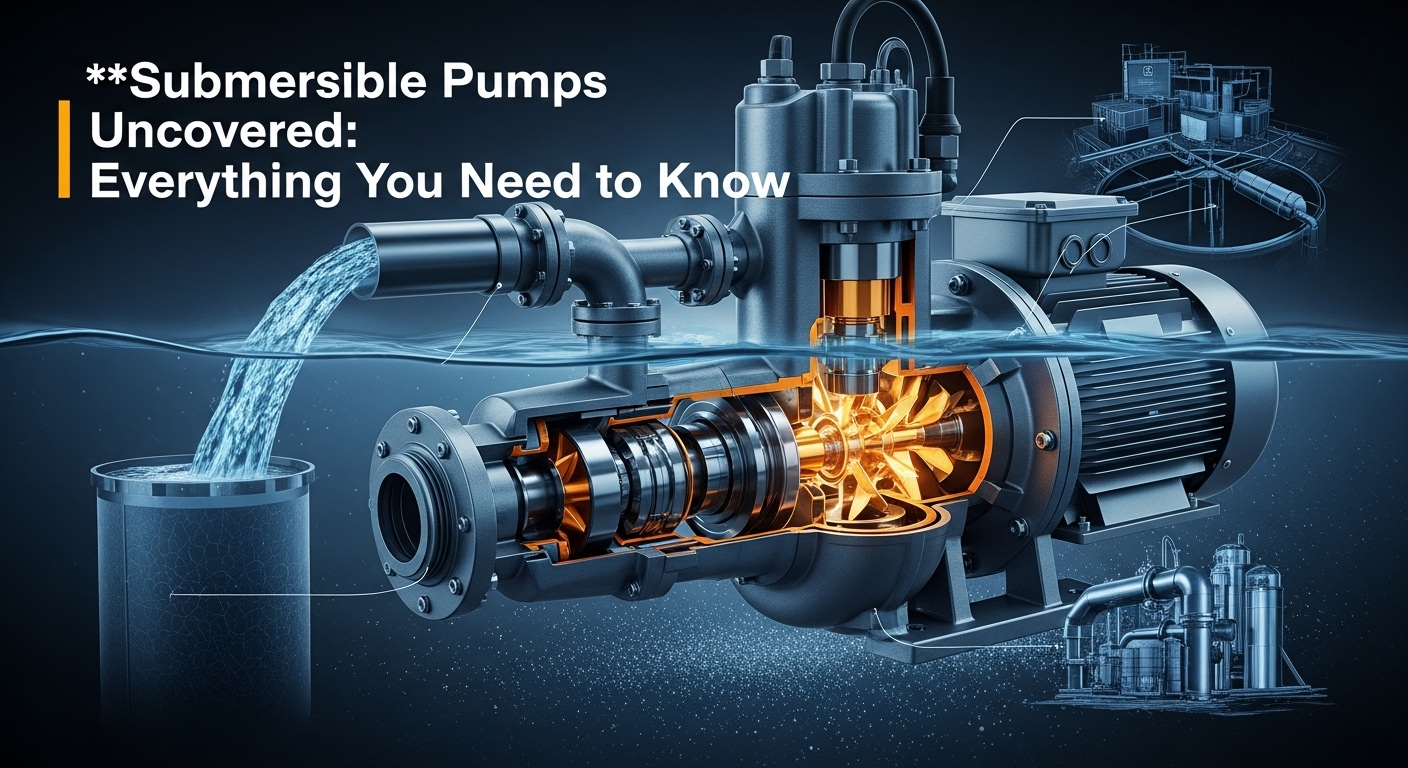
The effectiveness of submersible pumps lies in precision engineering that combines durable materials, advanced sealing systems, optimized hydraulic design, and high-efficiency motors. These elements ensure long service life, reduced maintenance, and dependable operation in demanding environments such as deep wells, wastewater systems, mining sites, and industrial processing plants.
Materials and Construction
The construction materials of submersible pumps play a vital role in determining performance, durability, and application suitability. Pumps designed for clean water applications often use stainless steel or cast iron, while those exposed to abrasive or corrosive fluids require hardened alloys, duplex stainless steel, or specialized coatings. Proper material selection enhances resistance to corrosion, erosion, and chemical attack, ensuring consistent performance and lower lifecycle costs.
Sealing Systems
Sealing systems are critical to protecting the motor from fluid ingress. High-quality mechanical seals, often arranged in tandem or cartridge configurations, prevent leaks even under high pressure. Advanced seal designs significantly improve reliability in applications involving wastewater, chemicals, or suspended solids.
Impeller Design
The impeller is the core hydraulic component of a submersible pump, directly influencing flow rate and efficiency. Depending on the application, pumps may use closed, semi-open, or vortex impellers. Wastewater and sludge handling systems often rely on non-clog or vortex impellers to prevent blockages while maintaining steady flow.
Motor Engineering
Submersible pump motors are compact, hermetically sealed, and designed for efficient heat dissipation in submerged conditions. These motors are engineered to operate continuously without overheating, ensuring stable output in applications such as irrigation, sewage pumping, and industrial fluid transfer.
Innovative Technologies
Modern submersible pumps integrate advanced technologies that improve performance, reliability, and energy efficiency. Features such as smart motor protection, condition monitoring, and optimized hydraulic profiles help reduce downtime and operating costs while extending equipment lifespan.
Agriculture and Irrigation
In agriculture, submersible water pumps provide a reliable solution for irrigation, groundwater extraction, and field drainage. Designed for continuous operation, these pumps ensure consistent water supply, reduce energy consumption, and support efficient crop production, especially in regions facing water scarcity.
Mining and Construction
Submersible dewatering pumps are essential in mining and construction projects where groundwater and surface water must be removed to maintain safe working conditions. These pumps are engineered to handle abrasive particles, high solids content, and challenging operating environments.
Municipal and Wastewater Management
Municipal infrastructure relies heavily on submersible sewage pumps to transport wastewater from residential and commercial areas to treatment facilities. These systems are designed for continuous operation and high solids handling, minimizing the risk of blockages and reducing maintenance requirements.
Environmental Management
In environmental and remediation projects, submersible pumps play a key role in managing polluted water bodies. Submersible sludge pumps are used to remove sediments, organic waste, and contaminants, supporting lake restoration, pond cleaning, and wastewater treatment processes.
Industrial Applications
Industrial facilities depend on submersible pumps to handle aggressive fluids, including chemicals, hot effluents, and oil-based liquids. Pumps designed for industrial use feature corrosion-resistant materials and robust construction, ensuring safe and efficient fluid transfer in chemical processing, power generation, and manufacturing plants.
Innovative Uses
Beyond conventional applications, submersible pumps are increasingly used in geothermal systems and renewable energy projects. Their ability to operate under extreme conditions makes them suitable for circulating fluids in energy extraction and sustainable infrastructure systems.
Conclusion
The design and engineering of submersible pumps focus on achieving high efficiency, long service life, and minimal maintenance. Through advanced materials, precision motor engineering, and innovative hydraulic design, submersible pumps continue to meet the evolving demands of agriculture, industry, municipalities, and environmental management, making them an indispensable solution for modern fluid handling challenges.